Positive displacement pumps move fluids at a constant rate regardless of pressure. Centrifugal pumps vary flow rate with pressure.
Positive displacement pumps and centrifugal pumps serve distinct purposes in fluid handling. Positive displacement pumps are ideal for high-viscosity fluids and precise flow control. They deliver a consistent volume per cycle, making them suitable for applications requiring steady flow. Centrifugal pumps excel in transferring large volumes of low-viscosity fluids.
They are efficient for applications needing variable flow rates based on pressure changes. Understanding the differences between these pumps helps in selecting the right one for specific industrial needs. Choosing the correct pump type improves efficiency, reduces operational costs, and ensures optimal performance in various applications.
Pump Basics
Pump Basics are crucial in understanding the differences between Positive Displacement Pumps and Centrifugal Pumps. Both types serve unique purposes and are essential in various industries. Knowing how each pump works can help in making informed decisions for your specific needs.
Introduction for Positive Displacement Pump Vs Centrifugal
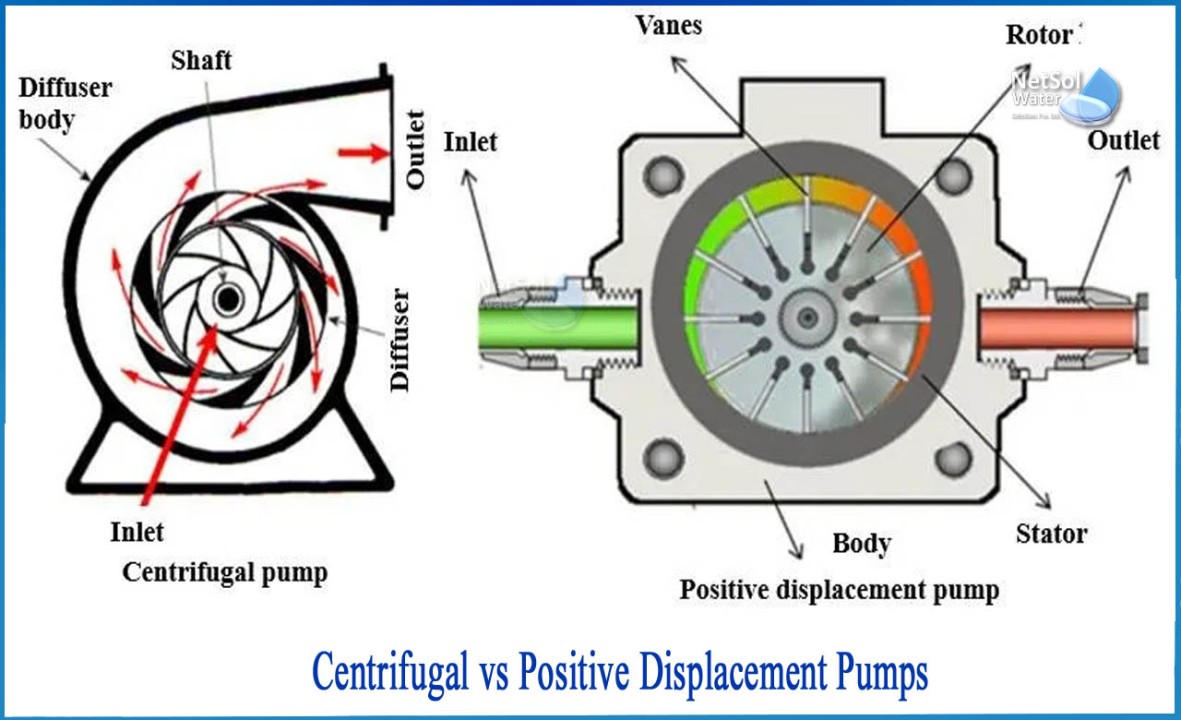
What Is A Positive Displacement Pump?
A Positive Displacement Pump moves fluid by trapping a fixed amount and forcing (displacing) that trapped volume into the discharge pipe. These pumps are known for their ability to handle high-viscosity fluids and deliver a constant flow regardless of pressure changes.
Here are some key features of Positive Displacement Pumps:
- Constant Flow Rate: Delivers a fixed volume of fluid with each cycle.
- High Pressure: Capable of generating high pressures, making them ideal for thick fluids.
- Self-Priming: Can remove air from the lines, making them efficient in various conditions.
Positive Displacement Pumps come in several types:
| Type | Features | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Gear Pumps | Uses gears to transfer fluid | Hydraulic fluid power, chemical mixing |
| Diaphragm Pumps | Uses a diaphragm to pump fluid | Wastewater treatment, chemical dosing |
| Rotary Vane Pumps | Uses vanes that move in and out of slots | Refrigeration, aviation fuel transfer |
What Is A Centrifugal Pump?
A Centrifugal Pump uses a rotating impeller to move water or other fluids by using centrifugal force. These pumps are highly efficient for transferring low-viscosity liquids at high flow rates. They are commonly used in various applications due to their simplicity and effectiveness.
Key features of Centrifugal Pumps include:
- High Flow Rate: Ideal for applications requiring the rapid movement of fluid.
- Simple Design: Fewer moving parts, making them easier to maintain.
- Variable Pressure: Flow rate changes with pressure, unlike Positive Displacement Pumps.
Centrifugal Pumps also come in different types:
| Type | Features | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Single-Stage Pumps | One impeller for simple operations | Water supply, irrigation |
| Multi-Stage Pumps | Multiple impellers for higher pressure | Boiler feed, mine dewatering |
| Axial Flow Pumps | Fluid moves parallel to the pump shaft | Flood control, drainage systems |
These basics will help you in choosing the right pump for your specific needs. Both Positive Displacement Pumps and Centrifugal Pumps offer unique advantages tailored to different applications.
Credit: www.linkedin.com
Operating Principles
Choosing between a positive displacement pump and a centrifugal pump can be challenging. Understanding their operating principles helps make an informed decision. Both pump types move fluids, but they do so in different ways. Let’s explore how each one works.
How Positive Displacement Pumps Work
Positive displacement pumps move fluid by trapping a fixed amount and forcing it through the discharge pipe. These pumps are ideal for high-viscosity fluids and high-pressure applications. They operate on a simple principle: capturing and moving fluid.
Here are the key points:
- Positive displacement pumps have constant flow, regardless of pressure.
- They are suitable for high-pressure applications.
- These pumps handle viscous fluids effectively.
There are two main types of positive displacement pumps:
- Rotary Pumps: These include gear, lobe, and screw pumps. They use rotating mechanisms to move fluid.
- Reciprocating Pumps: These include piston, diaphragm, and plunger pumps. They use a back-and-forth motion to move fluid.
Positive displacement pumps are efficient and versatile. They maintain a steady flow rate, making them reliable for various applications.
How Centrifugal Pumps Work
Centrifugal pumps use a rotating impeller to move fluid. The impeller’s rotation creates centrifugal force, pushing fluid outward. These pumps are ideal for low-viscosity fluids and high-flow applications.
Key features include:
- Centrifugal pumps are suitable for high-flow applications.
- They handle low-viscosity fluids effectively.
- The flow rate changes with pressure variations.
There are different types of centrifugal pumps:
- Single-stage Pumps: These have one impeller and are suitable for low to moderate head applications.
- Multi-stage Pumps: These have multiple impellers and are ideal for high-head applications.
Centrifugal pumps offer simplicity and efficiency. They are widely used in various industries, including water supply, chemical processing, and HVAC systems.
The operating principles of both positive and non positive displacement pumps help in making an informed decision. Whether you need a pump for high pressure or high flow, knowing how they work ensures you choose the right one.
Applications
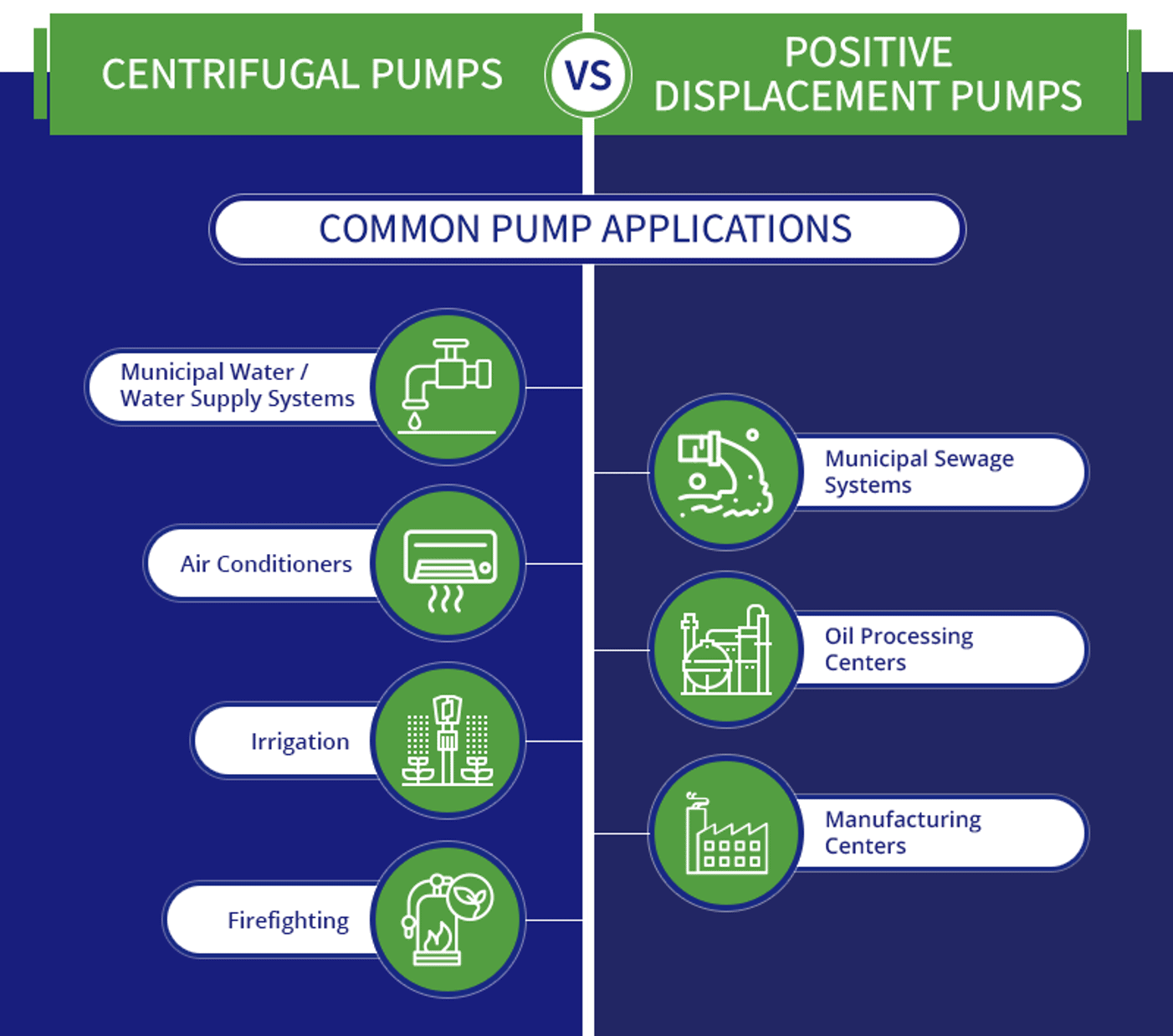
Positive Displacement Pumps and Centrifugal Pumps serve various applications in different industries. Each type of pump has unique features that make it suitable for specific tasks. Understanding the common uses of these pumps can help you choose the right one for your needs.
Common Uses Of Positive Displacement Pumps
Positive Displacement Pumps are known for their ability to handle high viscosity fluids and maintain a constant flow. They are widely used in industries where precise dosing or high pressure is required.
Here are some of the common applications:
- Chemical Processing: These pumps handle corrosive and viscous chemicals efficiently.
- Food and Beverage: They ensure accurate dosing and gentle handling of products.
- Oil and Gas: Essential for transferring crude oil and other viscous fluids.
- Pharmaceuticals: Used for precise dosing of medications and ingredients.
- Water Treatment: Ideal for metering chemicals and other additives.
| Industry | Application |
|---|---|
| Chemical Processing | Handling corrosive and viscous chemicals |
| Food and Beverage | Accurate dosing and gentle product handling |
| Oil and Gas | Transferring crude oil and viscous fluids |
| Pharmaceuticals | Precise dosing of medications |
| Water Treatment | Metering chemicals and additives |
The ability to maintain a constant flow rate makes Positive Displacement Pumps a preferred choice for many critical applications.
Common Uses Of Centrifugal Pumps
Centrifugal Pumps are popular for their efficiency and ability to handle large volumes of low viscosity fluids. They are commonly used in situations where a continuous flow is required.
Some typical applications include:
- Water Supply: Used in municipal water supply systems.
- Irrigation: Essential for large-scale agricultural irrigation systems.
- HVAC Systems: Integral to heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems.
- Industrial Processes: Moving water and other fluids in various processes.
- Fire Protection: Critical for fire sprinkler and hydrant systems.
| Industry | Application |
|---|---|
| Water Supply | Municipal water supply systems |
| Irrigation | Large-scale agricultural systems |
| HVAC Systems | Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning |
| Industrial Processes | Moving water and fluids |
| Fire Protection | Fire sprinkler and hydrant systems |
The efficiency and ability to handle large volumes make Centrifugal Pumps ideal for many industries and applications.
Performance Characteristics
Choosing the right pump for your application can be challenging, especially when comparing Positive Displacement Pumps and Centrifugal Pumps. Each type of pump has distinct performance characteristics that affect their suitability for different tasks. Understanding these characteristics helps in making an informed decision.
Flow Rate In Positive Displacement Pumps
Positive Displacement Pumps are known for their consistent flow rate. These pumps maintain a steady flow regardless of pressure changes. This makes them ideal for applications requiring precise dosing or metering. The flow rate in these pumps is directly proportional to the pump’s speed.
- Constant Flow: The flow rate remains unaffected by system pressure.
- Speed Dependent: Increasing the pump speed increases the flow rate.
- Volume Per Cycle: Each cycle moves a fixed volume of fluid.
The table below illustrates the typical flow rates for different types of Positive Displacement Pumps:
| Type of Positive Displacement Pump | Flow Rate (GPM) |
|---|---|
| Gear Pump | 5 – 500 |
| Diaphragm Pump | 0.3 – 300 |
| Piston Pump | 0.1 – 100 |
Positive Displacement Pumps are often used in applications where a precise and consistent flow rate is crucial, such as in chemical processing, food and beverage industries, and pharmaceuticals.
Flow Rate In Centrifugal Pumps
Centrifugal Pumps, on the other hand, have a variable flow rate that depends on the system’s pressure. As the pressure increases, the flow rate decreases. This characteristic makes them suitable for applications where the demand for flow can change.
- Variable Flow: The flow rate changes with system pressure.
- Pressure Dependent: Higher system pressure results in a lower flow rate.
- Dynamic Response: These pumps adjust the flow rate dynamically based on system needs.
The table below shows typical flow rates for various Centrifugal Pumps:
| Type of Centrifugal Pump | Flow Rate (GPM) |
|---|---|
| Single-Stage Pump | 10 – 5000 |
| Multistage Pump | 5 – 800 |
| Axial Flow Pump | 1000 – 100,000 |
Centrifugal Pumps are widely used in water supply, HVAC systems, and irrigation due to their ability to handle varying flow demands efficiently.
Efficiency Factors
Pumps are essential in various industries for moving fluids. Two common types are Positive Displacement Pumps and Centrifugal Pumps. Understanding their efficiency factors helps in selecting the right pump for specific applications.
Efficiency Of Positive Displacement Pumps
Positive Displacement Pumps work by trapping a fixed amount of fluid and forcing it through the pump. These pumps are highly efficient in handling high-viscosity fluids and maintaining constant flow rates. Here are some key points about their efficiency:
- Constant Flow Rate: They deliver a consistent flow regardless of pressure changes.
- High Viscosity Fluids: They handle thick fluids more efficiently than centrifugal pumps.
- Low Energy Consumption: They use less energy when moving high-viscosity fluids.
- Self-Priming: They can start and operate without requiring a pre-filled suction line.
These pumps are ideal for applications requiring precise volume control. Their efficiency is less affected by changes in pressure and viscosity. Positive Displacement Pumps maintain high efficiency across a wide range of conditions.
| Efficiency Factor | Positive Displacement Pumps |
|---|---|
| Flow Rate | Consistent |
| Viscosity Handling | High |
| Energy Consumption | Low |
| Self-Priming | Yes |
Efficiency Of Centrifugal Pumps
Centrifugal Pumps use a rotating impeller to move fluid. Their efficiency depends on several factors such as fluid properties and operating conditions. Key points about their efficiency include:
- Variable Flow Rate: Flow rate changes with pressure changes.
- Low Viscosity Fluids: They are more efficient with thin, water-like fluids.
- Higher Energy Consumption: Energy usage increases with fluid viscosity.
- Non-Self-Priming: They require a filled suction line to start operation.
Centrifugal Pumps excel in applications where a high flow rate is needed with low-viscosity fluids. They are less efficient with high-viscosity fluids. Their efficiency peaks at specific flow rates and pressures. Centrifugal Pumps are suitable for large-scale applications with consistent fluid properties.
| Efficiency Factor | Centrifugal Pumps |
|---|---|
| Flow Rate | Variable |
| Viscosity Handling | Low |
| Energy Consumption | High |
| Self-Priming | No |
Maintenance Needs
Both Positive Displacement Pumps and Centrifugal Pumps are critical in various industrial applications. To keep them running efficiently, understanding their maintenance needs is essential. Regular maintenance ensures longevity, reduces downtime, and enhances performance. Let’s explore the maintenance requirements for each type of pump.
Maintenance For Positive Displacement Pumps
Maintaining Positive Displacement Pumps involves several key steps. These pumps have many moving parts, requiring regular checks and lubrication. Neglecting maintenance can lead to wear and tear, reducing the pump’s efficiency.
Routine checks:
- Inspect seals and gaskets for leaks.
- Check for unusual noises or vibrations.
- Ensure the pump is not running dry.
- Monitor the temperature of the pump housing.
Lubrication:
Regular lubrication of moving parts is crucial. Use the manufacturer’s recommended lubricants. Over-lubrication can cause overheating, while under-lubrication can lead to wear and tear.
Replacement parts:
Replace worn-out parts like seals, bearings, and gears promptly. Keeping a stock of spare parts can minimize downtime.
Here’s a quick overview of the maintenance needs:
| Task | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Inspect seals and gaskets | Monthly |
| Lubricate moving parts | Bi-weekly |
| Check for unusual noises | Weekly |
| Replace worn-out parts | As needed |
Maintenance For Centrifugal Pumps
Centrifugal Pumps require a different maintenance approach. These pumps are simpler in design but still need regular attention to ensure optimal performance. Regular maintenance helps in preventing major breakdowns and extends the pump’s life.
Routine inspections:
- Check for leaks in the casing and seals.
- Inspect the impeller for wear and tear.
- Ensure the pump is primed properly before operation.
- Monitor vibration levels during operation.
Cleaning:
Clean the pump casing and impeller regularly. Debris can cause blockages and reduce efficiency.
Alignment:
Ensure the pump and motor are properly aligned. Misalignment can cause excessive wear on the bearings and seals.
Here’s a quick overview of the maintenance needs:
| Task | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Inspect for leaks | Monthly |
| Clean pump casing | Bi-weekly |
| Check impeller | Quarterly |
| Ensure proper alignment | Monthly |
Cost Considerations
When comparing Positive Displacement Pumps and Centrifugal Pumps, cost considerations play a crucial role in decision-making. Each type of pump has its own initial cost factors that can impact your budget and overall project expenditure. Understanding these differences helps in making an informed choice.
Initial Costs Of Positive Displacement Pumps
Positive Displacement Pumps generally have a higher initial cost. This is due to their complex construction and precise engineering. The components and materials required for these pumps are often high-quality to ensure durability and efficiency. Here are some key points to consider:
- Higher Material Costs: Positive Displacement Pumps use premium materials, such as stainless steel, to handle high pressure and abrasive fluids.
- Complex Design: The intricate design and multiple moving parts increase the manufacturing costs.
- Specialized Features: Features like variable flow rates and high-pressure capabilities add to the cost.
Here’s a quick comparison table for better understanding:
| Cost Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Material | High-quality materials increase durability but add to cost. |
| Design | Complex designs require precise manufacturing, raising costs. |
| Features | Specialized features lead to higher initial expenses. |
Initial Costs Of Centrifugal Pumps
Centrifugal Pumps usually have a lower initial cost. They are simpler in design and easier to manufacture. This makes them more budget-friendly. Here are some points to consider:
- Lower Material Costs: They often use less expensive materials compared to Positive Displacement Pumps.
- Simpler Design: Fewer moving parts and simpler construction reduce manufacturing costs.
- Standard Features: They typically come with standard features, making them less expensive.
Below is a comparison table for clarity:
| Cost Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Material | Less expensive materials lower the overall cost. |
| Design | Simple designs are easier and cheaper to produce. |
| Features | Standard features make them more affordable. |
Credit: www.gainesvilleindustrial.com
Choosing The Right Pump
Choosing the right pump is crucial for achieving optimal performance in various applications. Positive displacement pumps and centrifugal pumps serve different purposes. Understanding their key features and use cases can help in making the best choice for your specific needs.
When To Use Positive Displacement Pumps
Positive displacement pumps are ideal for applications requiring a constant flow rate. These pumps are perfect when handling high-viscosity fluids or precise dosing. They ensure the same volume of fluid is moved with each cycle, regardless of pressure.
Key scenarios for using positive displacement pumps:
- High-Viscosity Fluids: These pumps excel in moving thick liquids like oils, syrups, and slurries.
- Precise Dosing: They are excellent for applications needing precise amounts of liquid, such as in pharmaceuticals.
- Constant Flow Rate: Ideal for systems requiring a steady flow, regardless of pressure changes.
Comparison of Positive Displacement Pumps:
| Feature | Positive Displacement Pumps |
|---|---|
| Flow Rate | Constant |
| Fluid Viscosity | High |
| Pressure Handling | High |
| Applications | Pharmaceuticals, Food Processing |
When To Use Centrifugal Pumps
Centrifugal pumps are best for applications where large volumes of fluid need to be moved quickly. They are highly efficient and work well with low-viscosity fluids. These pumps use a rotating impeller to create flow, making them suitable for various industries.
Key scenarios for using centrifugal pumps:
- Low-Viscosity Fluids: Ideal for moving water, solvents, and other thin liquids.
- High Flow Rates: Perfect for applications requiring the rapid movement of large fluid volumes.
- Cost-Effective: Generally more affordable and easier to maintain than positive displacement pumps.
Comparison of Centrifugal Pumps:
| Feature | Centrifugal Pumps |
|---|---|
| Flow Rate | Variable |
| Fluid Viscosity | Low |
| Pressure Handling | Low to Medium |
| Applications | Water Supply, Irrigation |
FAQ
When comparing Positive Displacement Pumps and Centrifugal Pumps, many questions arise. Understanding these FAQs helps in choosing the right pump for your needs. Let’s dive into some common questions.
What Is A Major Advantage Of A Positive Displacement Pump Over A Centrifugal Pump?
Positive displacement pumps can handle viscous fluids better. They maintain a consistent flow regardless of pressure changes. This makes them ideal for thick fluids or fluids with suspended solids.
What Are The Disadvantages Of Positive Displacement Pumps?
Positive displacement pumps are often bulkier. They can be more expensive to maintain. They can also be noisy and require regular maintenance. These pumps can be less efficient with thin fluids.
When To Use A Positive Displacement Pump?
Use a positive displacement pump when you need a consistent flow rate. They are perfect for high-viscosity fluids. They also work well with fluids containing solids.
Why Are Centrifugal Pumps Used More Often Than Positive Displacement Pumps?
Centrifugal pumps are simpler and cheaper. They handle large volumes and work well with low-viscosity fluids. They are also quieter and require less maintenance.
Which Is Better Centrifugal Or Positive Displacement Pump?
It depends on your needs. For thick fluids, use a positive displacement pump. For large volumes of thin fluids, a centrifugal pump is better.
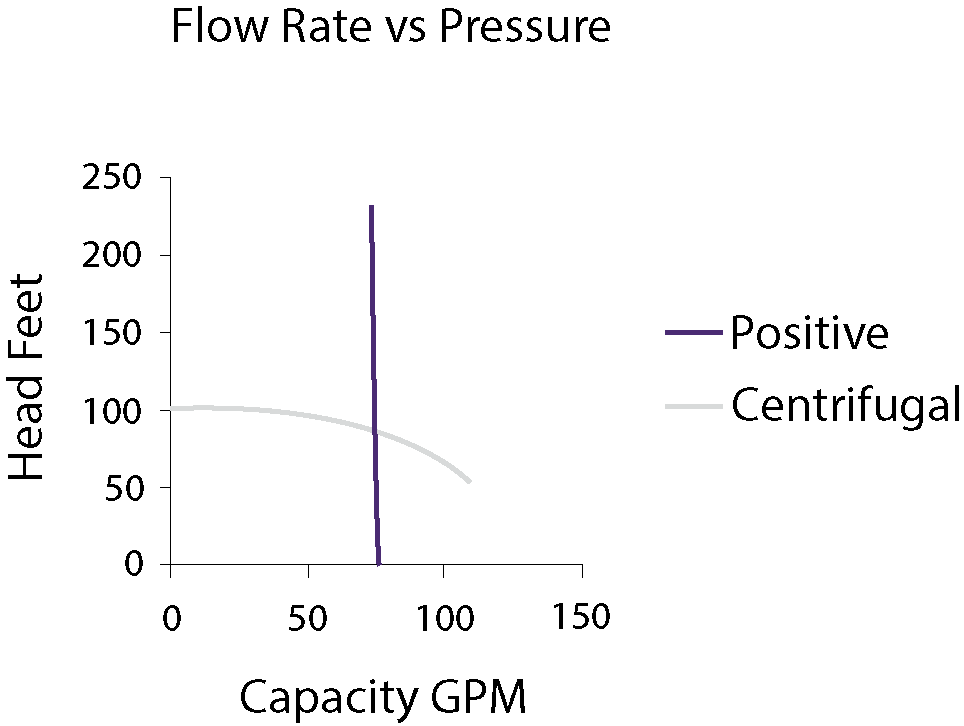
Credit: www.castlepumps.com
Conclusion
Choosing between a positive displacement pump and a centrifugal pump depends on your specific needs. Evaluate factors like fluid type, pressure, and flow rate. Both pumps have unique advantages. Understanding these differences helps you make an informed decision. Always consider your application requirements for optimal pump performance.