Electric water pumps offer efficient cooling and are energy-saving, while mechanical pumps are reliable and simpler in design. Understanding the differences between these two types of pumps is crucial for optimal vehicle performance.
Choosing the right water pump for your vehicle plays a significant role in its cooling system’s efficiency. Electric water pumps are known for their precision in controlling engine temperature, leading to better fuel economy and reduced emissions. On the other hand, mechanical water pumps have been the standard in the automotive industry for decades, praised for their durability and straightforward functionality.
These pumps operate directly off the engine’s power, making them less complex and often more robust. This brief comparison highlights the importance of considering both the vehicle’s needs and the benefits each pump type offers. Selecting the appropriate water pump can lead to improved vehicle performance, longevity, and overall satisfaction.
Credit: www.streetmusclemag.com
Introduction To Water Pumps
Electric water pumps and mechanical water pumps serve a vital role in modern technology. Both types ensure that fluids move efficiently from point A to point B. Understanding how these pumps work and their differences is crucial. This introduction explores the world of water pumps, shedding light on their functions and importance.
Types Of Water Pumps
Water pumps come in various designs, each with unique features suited for specific tasks. The primary distinction lies between electric water pumps and mechanical water pumps.
- Electric Water Pumps: These pumps use electric motors to generate the force needed to move water. They are known for their efficiency and control.
- Mechanical Water Pumps: Typically powered by engines or turbines, these pumps rely on mechanical force to operate. They are often found in vehicles and industrial machines.
Submersible pumps and centrifugal pumps are common types of electric pumps. On the other hand, gear pumps and diaphragm pumps often fall into the mechanical category.
Here’s a quick comparison:
| Type | Power Source | Common Use |
|---|---|---|
| Electric | Electric motor | Residential water supply |
| Mechanical | Engine/Turbine | Automotive cooling |
| Submersible | Electric motor | Deep wells, sumps |
| Centrifugal | Electric motor | Water circulation |
| Gear | Engine power | Oil, chemicals |
| Diaphragm | Engine power | High-viscosity fluids |
Common Applications
Water pumps serve countless applications, essential in both everyday life and specialized industries.
- Home Use: Electric pumps pull water from wells or push tap water into homes.
- Agriculture: Both pump types irrigate crops by delivering water across vast fields.
- Automotive: Mechanical pumps cool engines, preventing overheating.
- Industrial: Pumps in factories move chemicals, wastewater, and hot liquids.
Each application demands specific pump features. For example, electric submersible pumps are ideal for draining flooded areas due to their underwater operation. Conversely, mechanical diaphragm pumps handle thick fluids in chemical processing.
Check out this list of common pump applications:
| Application | Pump Type | Reason for Use |
|---|---|---|
| Residential Water Supply | Electric | Efficiency, control |
| Vehicle Cooling Systems | Mechanical | Engine integration |
| Flood Control | Submersible Electric | Underwater use |
| Industrial Processing | Diaphragm Mechanical | Handles viscous fluids |
| Agricultural Irrigation | Various | Area coverage, durability |
| Chemical Factories | Gear/ Diaphragm Mechanical | Chemical resistance |
Electric Water Pumps
The battle between Electric Water Pumps and Mechanical Water Pumps is one of efficiency and innovation. Electric water pumps stand out as modern solutions for cooling systems in various applications. These devices offer precise control and are often more compact than their mechanical counterparts. Let’s explore the world of electric water pumps and discover what makes them tick.
Working Mechanism
Electric water pumps function on a straightforward principle. They are powered by an electric motor instead of being driven by a belt connected to the engine. This design allows for their operation to be independent of engine speed, which leads to a consistent flow of coolant. Key components include:
- Electric Motor: Drives the pump.
- Impeller: Moves the coolant.
- Electronics: Control the pump speed.
The typical setup of an electric water pump involves a control unit that responds to engine temperature and adjusts the pump’s speed accordingly. This ensures optimal engine performance and prevents overheating.

Benefit Of Electric Water Pump
The primary benefit of an electric water pump lies in its ability to regulate cooling based on the engine’s needs. Unlike mechanical pumps, which are limited by the engine’s RPM, electric pumps can vary their flow rate for better efficiency.
Other benefits include:
- Reduced Engine Load: Frees up horsepower.
- Improved Fuel Economy: Less engine drag.
- Better Engine Warm-Up: Faster temperature regulation.
- Longevity: Less wear since it’s not always running.
These pumps are also lighter and can be positioned flexibly within the engine bay, which aids in vehicle design and weight distribution.
Advantages
Electric water pumps boast several advantages over mechanical ones. These include:
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Enhanced Cooling | Adapts to different driving conditions. |
| Space-Saving | Compact and allows for better layout. |
| Weight Reduction | Contributes to overall vehicle lightness. |
| Energy Efficient | Uses power only when necessary. |
Their independence from the engine also means that they can continue to cool after the engine is turned off, preventing heat soak.
Limitations
Despite their perks, electric water pumps come with limitations. These challenges include:
- Higher Initial Cost: More expensive than mechanical pumps.
- Electrical Dependency: Rely on the vehicle’s electrical system.
- Complexity: More intricate components and controls.
It’s also important to consider that they require a well-maintained electrical system to operate effectively. Any failure in the electrical circuit can lead to pump malfunction.
Mechanical Water Pumps
Mechanical Water Pumps play a crucial role in keeping vehicle engines cool. Unlike electric water pumps, these traditional pumps are directly powered by the engine’s motion. They have been under the hoods of cars for decades, ensuring that the engine’s temperature stays in a safe range.
Mechanical water pumps use a simple, yet effective design to move coolant through the engine block, radiator, and hoses. This helps to maintain optimal operating conditions for the engine and prevents overheating.
Working Mechanism
The working mechanism of a mechanical water pump is straightforward. It connects to the engine via a belt and pulley system or sometimes directly to the crankshaft. When the engine runs, it turns the pump’s impeller. The impeller, which is a wheel with vanes, spins inside the pump’s housing.
This action draws coolant from the radiator and pushes it into the engine. The coolant absorbs heat from the engine and carries it back to the radiator where it releases the heat into the air. Here are key points of its mechanism:
- Direct Drive: The pump is usually driven by the engine’s crankshaft, making it reliable and consistent.
- Impeller Action: Its spinning impeller creates the necessary flow of coolant.
- Sealing: A gasket ensures that the coolant does not leak from the connection between the pump and the engine.
Advantages
Mechanical water pumps boast several advantages that have made them the standard in engine cooling for many years. Their direct connection to the engine guarantees performance in sync with engine speed, which can be beneficial in certain scenarios. Advantages include:
- Simplicity: They have fewer parts that could fail, making them simple and sturdy.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Generally cheaper to manufacture and replace compared to electric variants.
- No Electrical Load: Since they don’t require electrical power, they put no additional load on the vehicle’s electrical system.
- Proven Reliability: Decades of use in the automotive industry have proven their durability and reliability.
Limitations
Despite their advantages, mechanical water pumps have certain limitations. They are not without their drawbacks, which can affect overall engine efficiency and performance.
Some of these limitations are:
- Engine Load: They can place a significant load on the engine, which may reduce efficiency and power output.
- Fixed Flow Rate: The pump’s flow rate is tied to engine speed, which isn’t always ideal for all operating conditions.
- Wear and Tear: Being mechanical parts, they are subject to wear and may eventually fail, requiring replacement.
- Limited Control: Unlike electric pumps, mechanical pumps offer less flexibility in terms of speed control and on-demand operation.

Credit: www.idolz.com
Electric Water Pump Vs Mechanical Pump Pros And Cons
Deciding between an electric water pump and a mechanical pump is crucial for your vehicle’s cooling system. Each has its pros and cons. This guide explores those differences, helping you make an informed choice.
Pros Of Electric Water Pumps
- Improved Engine Performance: Electric pumps can boost horsepower by reducing engine drag.
- Better Cooling Efficiency: They offer precise control over coolant flow, enhancing cooling.
- Energy Efficiency: These pumps consume less power, contributing to fuel savings.
Cons Of Electric Water Pumps
- Higher Initial Cost: They are more expensive upfront than mechanical pumps.
- Complex Installation: Installing an electric pump can be more complicated, requiring electrical knowledge.
- Dependency on Electrical System: Their operation hinges on the vehicle’s electrical system’s reliability.
Pros Of Mechanical Water Pumps
- Reliability: With fewer parts, mechanical pumps are less likely to fail.
- Cost-effective: They are generally cheaper and easier to replace than electric pumps.
- Simple Installation: Mechanical pumps can be installed with basic tools and knowledge.
Cons Of Mechanical Water Pumps
- Reduced Efficiency: They can sap engine power, slightly lowering performance.
- Less Precision: Mechanical pumps offer less control over coolant flow.
- Constant Operation: These pumps work whenever the engine is running, sometimes unnecessarily.
Performance Comparison
Understanding the differences between electric and mechanical water pumps is key for anyone invested in vehicle performance or maintenance. These components play a crucial role in regulating an engine’s temperature, but they differ in operation and efficiency. Let’s dive into a detailed performance comparison to see how they stack up against each other.
Efficiency
Efficiency is a top concern when comparing electric and mechanical water pumps. An electric water pump is often seen as the more efficient option for several reasons:
- Consistent Flow: Electric pumps maintain a steady coolant flow, independent of engine RPM, leading to better thermal management.
- Variable Speed: They can adjust their speed to meet cooling demand, which is not possible with mechanical pumps.
- Reduced Engine Load: By running off electrical power, electric pumps take a load off the engine, potentially improving fuel economy.
On the other hand, mechanical water pumps are directly driven by the engine. Their performance varies with engine speed, which can lead to inefficiencies:
- RPM Dependent: At low RPMs, cooling is limited, while at high RPMs, the pump can work more than needed.
- Constant Drag: They add a constant load to the engine, which can reduce overall efficiency.
In comparison, a table summarizing the efficiency aspects:
| Feature | Electric Water Pump | Mechanical Water Pump |
|---|---|---|
| Coolant Flow | Consistent | Varies with RPM |
| Speed Control | Variable | Fixed |
| Engine Load | Reduced | Constant |
Power Consumption
When it comes to power consumption, both types of water pumps have their pros and cons:
Electric Water Pumps are praised for their smart use of power. They only consume electricity when needed and can shut off completely when the engine is cool. This selective use of energy can lead to overall power savings:
- Targeted Operation: Only runs when necessary, avoiding wasteful energy use.
- Battery Dependent: Relies on the vehicle’s electrical system, which can be a downside if the battery is weak.
Conversely, Mechanical Water Pumps are always in operation as long as the engine runs. This constant operation means they are always drawing power from the engine:
- Continuous Draw: Consumes engine power during operation, potentially affecting performance.
- No Electricity Needed: While they don’t rely on electricity, their unceasing demand on engine power can be a drawback.
A table to illustrate power consumption differences:
| Aspect | Electric Water Pump | Mechanical Water Pump |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Use | Only when cooling is needed | Constant, regardless of cooling needs |
| Dependency | Electrical system | Engine power |
Maintenance Needs
Electric Water Pump Vs Mechanical: Choosing the right pump for your vehicle affects its performance. Let’s talk about maintenance needs. Both electric and mechanical water pumps keep engines cool. But their care differs. Regular maintenance ensures they work well. Let’s dive into the specifics of each type.
Electric Pump Care
Electric water pumps are known for their efficiency and control. They demand less frequent check-ups compared to mechanical pumps. To maintain an electric water pump, follow these simple steps:
- Inspect Wiring: Check the wires for damage. Fix any issues to prevent electrical faults.
- Coolant Level: Ensure the coolant is full. Top up if necessary.
- Clean Contacts: Clean electrical contacts. This prevents corrosion and maintains good connections.
Electric pumps have fewer moving parts. This means less wear and tear. They often last longer than mechanical pumps. However, keep an eye on the electronic control unit (ECU). It may need updates or checks for fault codes.
A simple table can help you remember when to perform these tasks:
| Task | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Inspect Wiring | Every 6 months |
| Check Coolant Level | With each oil change |
| Clean Contacts | Annually |
| ECU Check | As needed |
Mechanical Pump Care
Mechanical water pumps rely on the engine’s power. They need more regular maintenance. To take care of a mechanical pump, consider these points:
- Belt Tension: Check the belt. It drives the pump. Adjust if it’s loose.
- Leak Inspection: Look for leaks. Seals can wear out. Replace them if you find drips.
- Bearing Noise: Listen for grinding sounds. They can signal bearing failure. Replace the pump if necessary.
Mechanical pumps work hard and wear out faster. They need more attention. Keep a close eye on the belt and pulley system. This is crucial for the pump’s operation.
A maintenance schedule can help:
| Task | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Check Belt Tension | Every 3 months |
| Inspect for Leaks | Every oil change |
| Listen for Bearing Noise | At the first sign of noise |
Remember, proper care extends the life of both pump types. Keep up with these tasks for a smooth ride.
Cost Analysis
Choosing between an electric water pump and a mechanical one involves looking at costs. We’ll explore both the initial investment and long-term costs. This will help you make a smarter choice for your car’s cooling system.
Initial Investment
Electric water pumps often have a higher purchase price than mechanical water pumps. But, there’s more to consider than just the price tag. Let’s break it down:
- Electric Water Pump:
- Higher upfront cost
- May require additional parts like a controller
- Mechanical Water Pump:
- Lower initial cost
- Generally, no extra parts needed
Here’s a simple table to compare:
| Type | Initial Cost | Extra Parts Needed |
|---|---|---|
| Electric Water Pump | High | Yes |
| Mechanical Water Pump | Low | No |
Even though electric pumps cost more initially, they can be a better choice for performance cars.
Long-term Costs
When looking at long-term costs, electric water pumps often come out ahead. Here’s why:
- Energy Efficiency: Electric pumps use power only when needed, saving fuel.
- Durability: They usually last longer than mechanical pumps, reducing replacement costs.
Let’s compare long-term costs:
- Electric Water Pump:
- Lower fuel costs due to efficiency
- Less frequent replacements needed
- Mechanical Water Pump:
- Higher fuel costs over time
- May need more frequent replacements
While the initial cost of an electric water pump might be higher, its efficiency and durability can lead to savings. These savings make electric pumps a cost-effective choice in the long run.
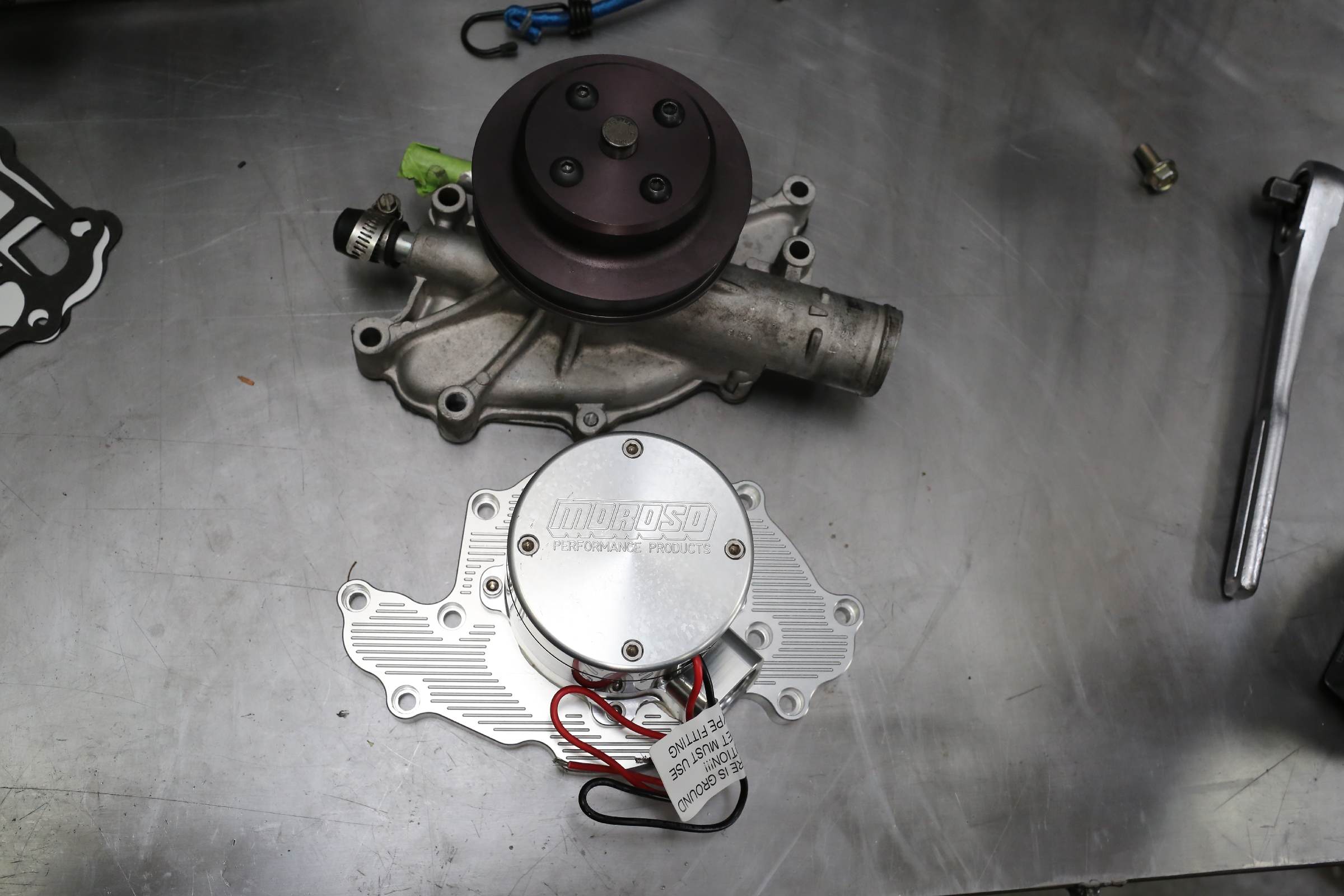

Credit: www.streetmusclemag.com
Environmental Impact
The debate between electric and mechanical water pumps often focuses on performance and cost. Yet, the environmental impact deserves attention too. Both types affect our planet differently. From the energy they consume to the noise they make, each pump has its own footprint. Let’s dive into the specifics and see how they stack up against each other in terms of environmental friendliness.
Energy Use
When we compare electric and mechanical water pumps, energy efficiency is a top concern. Electric water pumps are generally seen as more eco-friendly because they use less energy. They are designed to work on-demand, meaning they only operate when needed, reducing energy waste.
Here’s a closer look at how they save power:
- Smart operation: Electric pumps can adjust their speed based on the system’s needs, leading to significant energy savings.
- Battery-powered options: Some electric pumps can be paired with renewable energy sources, like solar panels, for a cleaner setup.
On the other hand, mechanical water pumps are constantly running, tied to an engine’s operation. This can lead to unnecessary energy use, especially during idle times.
A quick comparison:
| Water Pump Type | Energy Consumption | Eco-Friendly Rating |
|---|---|---|
| Electric | Lower | High |
| Mechanical | Higher | Low |
Noise Levels
Noise pollution is another environmental concern. Electric water pumps have the upper hand here, with their quiet operation. They make little noise, as they lack the mechanical parts that typically generate sound. This leads to a more peaceful environment.
Here’s why electric pumps are the quieter choice:
- Less vibration: Electric pumps have fewer moving parts, which means less noise from shaking and rattling.
- Soft humming: Instead of a loud roar, electric pumps often emit a low hum that is easy on the ears and wildlife.
Mechanical water pumps, in contrast, can be quite loud. They are connected to an engine that produces a constant noise while operating. This can be disturbing to both people and animals, especially in quiet areas.
Consider the following noise impact:
| Water Pump Type | Noise Level | Quietness Rating |
|---|---|---|
| Electric | Low | High |
| Mechanical | High | Low |
In summary, electric water pumps offer a greener choice with their efficient energy use and quiet performance. They stand out as a better option for those who value environmental sustainability.
Choosing The Right Pump
Electric and mechanical water pumps serve the same purpose: to move water through systems. Each type, however, suits different scenarios. The key to selecting the right pump lies in understanding the specific needs of your project. Consider the performance, efficiency, and durability of both pump types before making a decision.
Project Requirements
A pump’s fit for a project hinges on the system’s demands. Electric water pumps, known for their efficiency and control, work well in settings that need variable flow rates or remote operation. They are often lighter and require less maintenance. On the other hand, mechanical pumps, driven by an engine or motor, offer robust performance in constant-flow scenarios. They excel in environments where electrical power is unreliable or unavailable.
- Flow Rate: How much water needs to move, and how fast?
- Pressure Requirements: What force is necessary to move the water?
- Power Source: Is electricity readily available and reliable?
- Environment: Will the pump face harsh conditions?
| Feature | Electric Pump | Mechanical Pump |
|---|---|---|
| Efficiency | High | Varies |
| Control | Variable speed | Fixed speed |
| Maintenance | Lower | Higher |
| Durability | Depends on usage | Often higher |
Budget Considerations
Your budget will significantly influence the pump choice. An electric water pump may have a higher initial cost but can lead to savings over time due to its energy efficiency. Reflect on the long-term costs, such as energy consumption and maintenance, not just the purchase price. Mechanical pumps may cost less upfront, but their operation and upkeep can add up.
- Initial Cost: Is the purchase price within your budget?
- Energy Usage: How much will the pump cost to run?
- Maintenance Costs: What are the expected maintenance expenses?
- Life Span: How long will the pump last before replacement is needed?
| Cost Factor | Electric Pump | Mechanical Pump |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Price | Higher | Lower |
| Running Costs | Lower | Higher |
| Maintenance | Less frequent | More frequent |
| Life Expectancy | Varies | Often longer |
FAQs
When exploring the differences between electric and mechanical water pumps, many questions arise. These pumps, vital for vehicle cooling systems, differ in operation, efficiency, and maintenance.
Understanding these differences helps users make informed decisions for their specific needs. Let’s dive into some frequently asked questions to clarify the pros and cons of each type of water pump.
What Is Better, An Electric Or Mechanical Water Pump?
The better choice depends on usage. Electric water pumps are more efficient and reduce engine load, leading to improved performance and fuel economy. Mechanical pumps, on the other hand, are simple and robust, making them a reliable choice for many engines.
What Are The Disadvantages Of An Electric Water Pump?
- Higher upfront cost: Electric pumps can be more expensive than mechanical ones.
- Electrical dependency: They require a stable electrical system to operate.
- Complexity: Installation and wiring can be more complex than mechanical pumps.
Why Switch To An Electric Water Pump?
Switching to an electric water pump offers several benefits. These include improved engine cooling, reduced parasitic engine load, and the ability to operate independently of engine RPM. This leads to better performance and fuel efficiency.
Which Pump Is Better Manual Or Electric?
Electric pumps generally outperform manual pumps, offering consistent water flow and on-demand operation. They are ideal for modern vehicles where precision cooling is essential. In contrast, manual or mechanical pumps are less complex and more suited to older vehicles or simpler applications.
What Is The Lifespan Of An Electric Water Pump?
The lifespan of an electric water pump can vary, but it is typically between 60,000 to 90,000 miles. This is contingent on the quality of the pump and the conditions under which it operates. Regular maintenance can extend its life further.
Conclusion
Deciding between electric and mechanical water pumps depends on your needs. Electric pumps offer efficiency and are perfect for modern applications. Mechanical pumps shine for simplicity and reliability. Weigh your priorities to make the best choice for your system. Remember, the right pump ensures optimal performance and longevity.

